MongoDB Node Driver
Le pilote officiel MongoDB Node.js permet aux applications Node.js de se connecter à MongoDB et de travailler avec des données. Le pilote dispose d'une API asynchrone qui vous permet d'accéder aux valeurs de retour de méthode via Promises ou de spécifier des rappels pour y accéder lors de la communication avec MongoDB. (Traduction du site officiel)
Étape 1 - Ajout du module mongodb
- Créez un nouveau projet Node
- L’initialiser
-
Ajoutez le module mongodb :
-
Importer le module dans le repo approprié :
Étape 2 – Établissement de la connexion
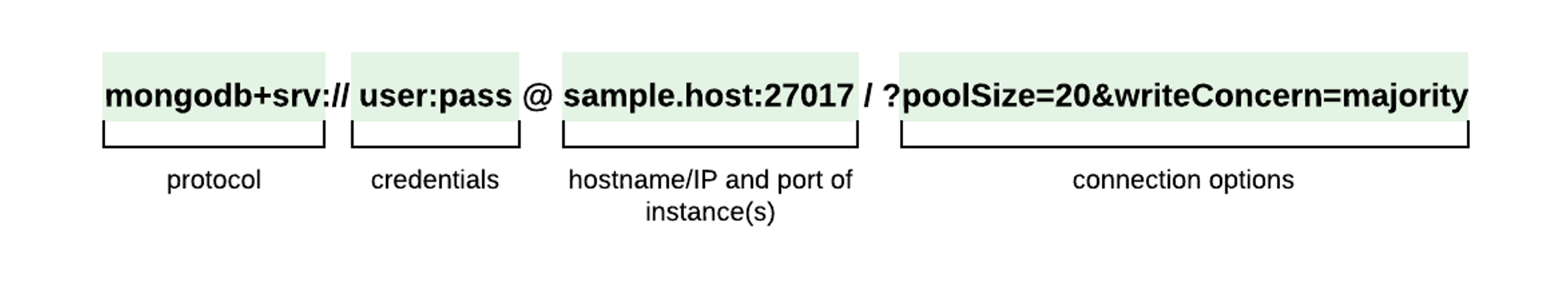
// connexion distante
const uri = "mongodb+srv://sample-hostname:27017/?poolSize=20&writeConcern=majority";
// connexion locale
const uri = "mongodb://localhost:<port>"
Étape 3 – Exécuter vos requêtes
Exemple : Utilisation dans une application Node.js (sans Express)
import { MongoClient } from "mongodb";
// Replace the uri string with your MongoDB deployment's connection string.
const uri = "mongodb+srv://<user>:<password>@<cluster-url>?retryWrites=true&writeConcern=majority";
const client = new MongoClient(uri);
async function run() {
try {
await client.connect();
const database = client.db('sample_mflix');
const movies = database.collection('movies');
// Query for a movie that has the title 'Back to the Future'
const query = { title: 'Back to the Future' };
const movie = await movies.findOne(query);
console.log(movie);
} finally {
// Ensures that the client will close when you finish/error
await client.close();
}
}
run().catch(console.dir);
Exemples d'utilisation
MongoDB cursor
Lorsque la requête retourne plusieurs résultats, ceux-ci sont retournés dans un curseur
Les fonctions suivantes retournent un curseur :
- Collection.find()
- Collection.aggregate()
- Collection.listIndexes()
- Db.listCollections()
- Db.aggregate()
Voici deux façons de parcourir un curseur :
La méthode toArray() permet d’obtenir un tableau à partir des documents d’un curseur. Cursor.toArray()
Note
Les bases de données utilisées dans cette leçon proviennent de ce dépôt GitHub